In recent years, there has been a significant advancement in the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Augmented Reality (AR). These technologies have become increasingly popular and have the potential to enhance virtual experiences in various fields such as gaming, education, healthcare, and...
AI Algorithm Learns to Detect Underground Water Using Satellite Imagery
A groundbreaking artificial intelligence system has demonstrated remarkable ability to identify underground water sources by analyzing satellite photographs, offering new hope for communities facing water scarcity around the globe. This technological breakthrough could transform how geologists and environmental scientists approach the critical challenge of finding freshwater reserves.
How the Technology Works
The algorithm processes multispectral satellite imagery, examining wavelengths invisible to the human eye. By analyzing subtle variations in surface temperature, vegetation patterns, and geological formations, the system can predict the presence of underground aquifers with unprecedented accuracy.
Key Detection Methods
The artificial intelligence employs several sophisticated techniques to locate subsurface water:
- Thermal anomaly detection that identifies cooler ground temperatures indicating water presence
- Vegetation index analysis recognizing plant growth patterns associated with accessible groundwater
- Geological feature recognition mapping fault lines and permeable rock formations
- Historical precipitation data correlation with current surface conditions
Development and Training Process
Researchers trained the neural network using thousands of confirmed water discovery sites from across multiple continents. The training dataset included successful well locations, known aquifer boundaries, and geological surveys spanning decades of fieldwork. This comprehensive approach allowed the algorithm to recognize patterns that even experienced hydrologists might overlook.
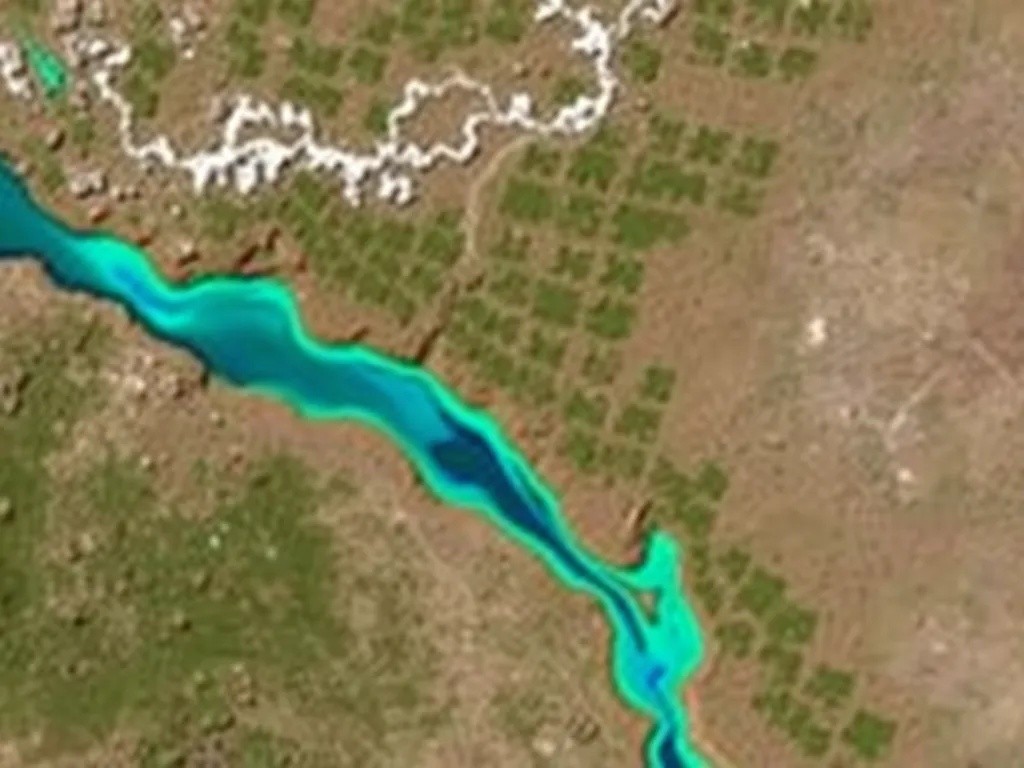

Impressive Accuracy Rates
Initial field tests have yielded remarkable results. The system correctly predicted underground water presence in approximately 87 percent of test locations, significantly outperforming traditional surveying methods. Perhaps more importantly, the algorithm reduced false positive rates by nearly sixty percent compared to conventional approaches.
Practical Applications
The implications of this technology extend far beyond academic research. Humanitarian organizations have already expressed interest in deploying the system to assist drought-affected communities in Africa and Central Asia. Agricultural enterprises see potential for optimizing irrigation well placement, while municipal authorities envision using the technology for urban water supply planning.
Environmental Considerations
Scientists emphasize that responsible water extraction remains paramount. The algorithm not only locates water sources but also estimates reservoir capacity and recharge rates, helping planners develop sustainable extraction strategies. This holistic approach addresses concerns about groundwater depletion that have plagued previous water development projects.
Future Development Plans
The research team continues refining the algorithm, incorporating new data sources including synthetic aperture radar and gravitational measurements. They anticipate releasing an open-access version of the basic detection system within the coming year, enabling researchers and aid organizations worldwide to benefit from this technological advancement.
As climate change intensifies pressure on global freshwater resources, innovations like this satellite-based detection system represent crucial tools for ensuring water security. The marriage of space technology and artificial intelligence offers a promising path forward in addressing one of humanity's most fundamental needs.



